What will you learn?
1.What are the long-term effects of the concluded El Niño phenomenon?
2. What are the consequences of record temperatures recorded after the end of El Niño?
3. How does drought affect water access in regions like the outskirts of Bogota?
4. What are scientists' concerns regarding the future of the global climate after the end of El Niño?
5. What actions are needed to adapt to and mitigate the effects of climate change caused by El Niño?
Tense water situation and temperature records
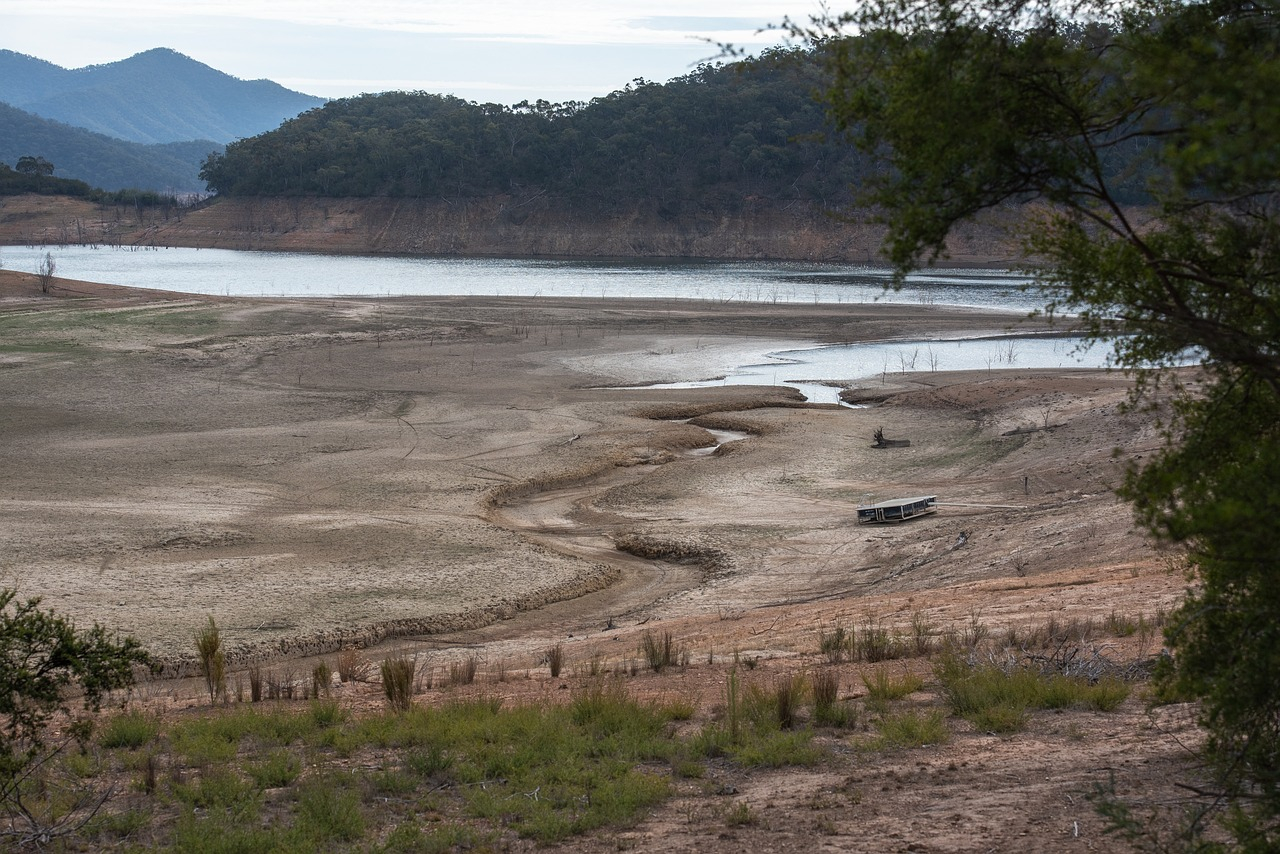
After the end of El Niño, droughts persist, and their effects are dramatically felt, for example, on the outskirts of Bogota in Colombia, where residents queue for water delivered by trucks. This is a direct result of prolonged rainfall deficits. This phenomenon illustrates the significant dependencies between global climate change and local crises. Data from the Copernicus Climate Change Service shows that recent months have been the warmest on record, further exacerbating difficulties in managing natural resources.
The climate future in light of observations
Climatologists emphasize that the coming months will be crucial for assessing how much El Niño influenced current weather anomalies and whether these temperature records will have a lasting impact on the Earth's climate. Concerns arise that changes in weather patterns may be permanent, leading to even greater frequency and intensity of climatic extremes. Such a situation requires detailed analysis and swift action from scientists and decision-makers to effectively counter long-term climate change.
In the context of these events, the legacy of El Niño is a reminder of the complex and deeply interconnected processes governing our global climate. Each such phenomenon is an opportunity to gather data invaluable in predicting future climate changes and planning appropriate adaptive and mitigative actions.