what you will learn
What does the successful launch of the Angara A5 mean for the Russian space program?
What plans does Russia have for building its own space station?
How will the Angara A5 rocket influence Russia's future missions and space research?
What technologies and transport capabilities does the Angara A5 rocket offer?
What ambitious goals is Russia setting in the context of space exploration following the successful launch of the Angara A5?
A New Chapter in Space Exploration
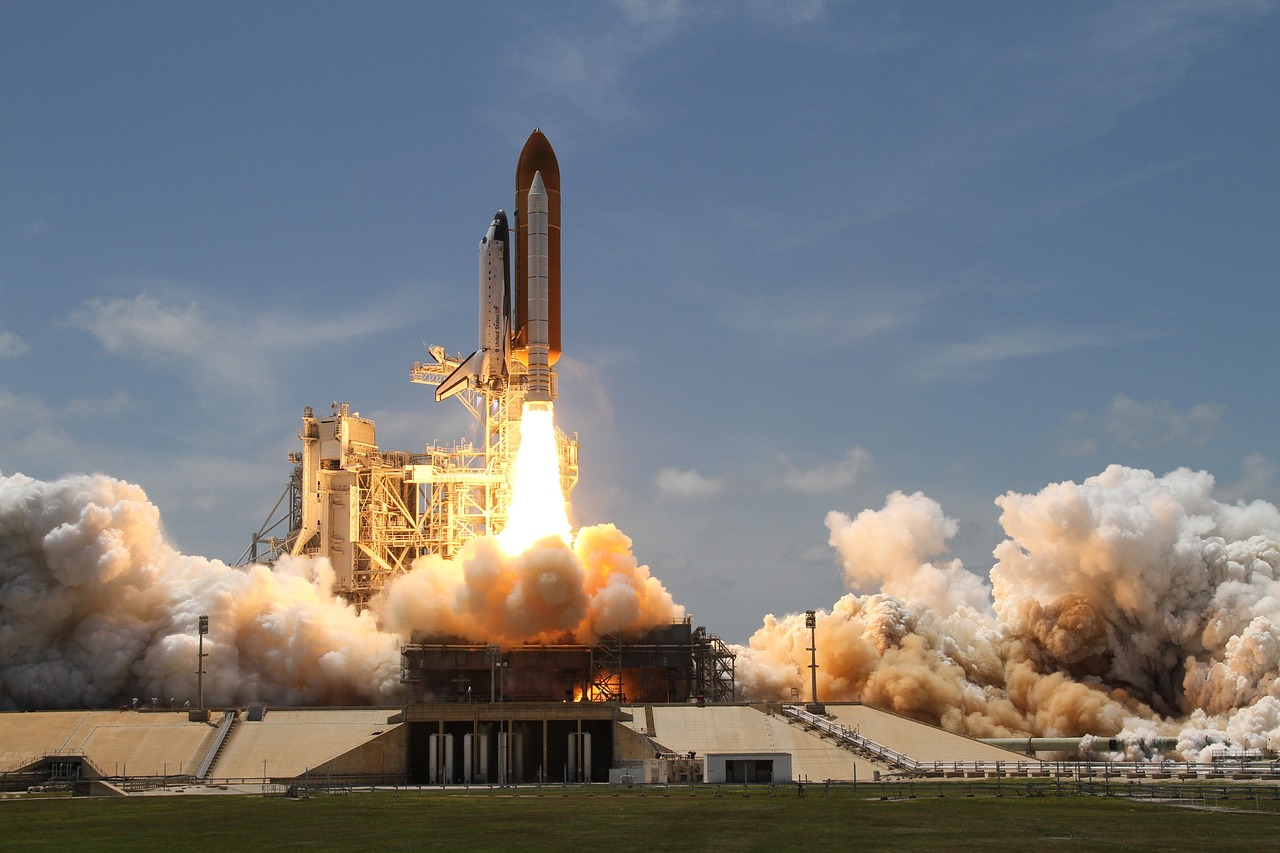
The Angara A5 rocket, bringing its cargo into orbit, becomes a key element of Russian space plans. Its success means not only a breakthrough in rocket technology but also a step forward in achieving ambitious goals such as independent manned missions and further space research. Russia, with its rich cosmic heritage in mind, sees in the Angara A5 a tool that will enable further investigations of the solar system and the development of technologies necessary for a long-term human presence in space.
Building a Competing Space Station
One of the most ambitious endeavors related to the success of the Angara A5 is the construction of a Russian space station that could compete with the ISS. This project, utilizing the extended transport capabilities of the Angara A5, would not only enable Russia to conduct independent space research but also strengthen its position on the international stage as one of the leaders in space exploration. The new space station would serve as a platform for many innovative research projects, from astrophysics to space biology, opening new perspectives for science and technology.
The success of the Angara A5 not only confirms Russia's technological capabilities but also opens new horizons in space exploration. From building a new space station, developing advanced technologies, to independent manned missions - Russia sets ambitious goals for the coming years. In the context of the global space race, the success of the Angara A5 could be a key moment that not only marks Russia's presence in space but also contributes to the development of international cooperation in space research.